CREATE YOUR WORKSPACE
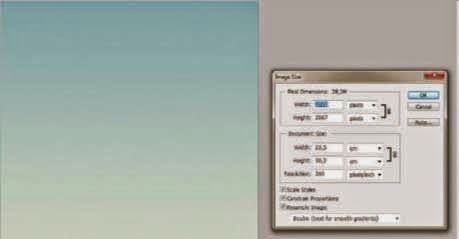
Create a new file 235mm wide by 302mm high at 300dpi. The background will be made using a gradient. Activate the Gradient tool and in the Gradient Editor choose a #e2ebdb colour in one Color Stop and #69adbf in the other. Then drag the Gradient tool line from the bottom edge to the upper edge.
First, select a model of your choice from any photo stock site. Open the Channels panel and select Blue. Ctrl/right-click then duplicate this. Go to Image>Adjustment>Levels and make a small adjustment to increase contrast. The main goal is to keep edges of the hair and not cut them off. Go to Image>Apply Image, choose Blending: Overlay.
PAINT TO YOUR CHANNEL
Paint the model with a black brush and the background with a white one, using different sizes of hard brush. Keep edges as they were in the original image. Cmd/Ctrl-click on the duplicate thumbnail and create a selection of all black areas. Turn on the visibility of the RGB channels and open the Layers window. Drag the model into your working file.
TRANSFORM ELEMENTS
Go to cgtextures.com, then search and download the large sized 12107 grass file. Drag this into your working file. Press Cmd/Ctrl+T, then Ctrl/right-click a control point and choose Perspective from the pop-up options. Narrow the upper control points then, without pressing enter, Ctrl/right-click again and choose Distort. Click the upper-middle point and lower it. After this, choose Warp and adjust like in the example presented, using points to create Bézier curves. Your goal is to make a curved surface.
Open ‘Pearl.psd’ and drag the layer into your image. Cmd/Ctrl+J to make a few duplicate layers of this. Use Transform to resize your layers and arrange on top of the grass layer, making sure that the bigger ones are closer and smaller ones further away. Use the Polygonal Lasso tool to select grass shapes and duplicate these from the grass texture layer. Place these new cut-out layers above your pearl ones. Add Layer>Layer Style>Inner Shadow to the biggest pearl layer, setting Opacity at 75%, Angle at -75 degrees, Distance at 20, Choke at 0 and Size at 109.
♦ QUICK TIP
Shade objects in your images more easily by working to a new layer Always place this directly above the one you want to edit. For better results, always lay your shadow marks with a Multiply blending mode. Also, before you start painting, load a selection of the layer below, then press Cmd/Ctrl+H to hide it.
Go to CG Textures and download the 24670 flowerbed file. Use the Pen tool to make a selection of your flowers, then drag them into your image. Since two flowers bushes are needed, duplicate your new layer and reposition the duplicate using the Transform tool. Now apply colour corrections. Select Image>Adjustment>Levels and input the following values: 0, 2.00 and 220. Apply a Hue/Saturation layer, setting Saturation at -50. Finally, apply a Color Balance adjustment layer at +8 , -31 and -28.
DECORATIVE THORNS
Create thorns by adding the Pen Path tool to a new layer. Select a 30px hard white brush and in the Paths panel, Ctrl/right-click your path thumbnail. Select Stroke with Simulate Pressure deactivated. Choose Select>Load Selection and use a soft brush at 15px, with Always Use Pressure For Opacity activated from the Brush options. Add shadows to the edges of your line, using a #b7b7b7 coloured brush on a new layer. Open ‘Thorns.psd’ and paste them in, arranging them on the stem you’ve created.
ANIMAL COLLAGE
Open the ‘Fawn.psd’, ‘Yellow Rose.psd’ and ‘Horns.psd’ from the disc. Select and drag them into your working image. Activate the Fawn layer and apply Color Balance, setting values to +48, -22 and -36. Activate the Horns layer and again add Color Balance, setting values to +66, -63 and -34. Create a new layer beneath your Yellow Rose layer and apply a #977166 colour to create a shadow. Do this by applying a soft brush with the Always Use Pressure For Opacity option active.
CREATE ARROWS
Make the body of your arrows by applying a selection with your Rectangular Marquee tool and filling this with a #404040 colour. Add an Inner Glow Layer Style and set Blend Mode to Screen, Color to #c3a87c, Technique to Softer, Source to Center, Size at 29 and Choke to 18. Use the Pen Shape tool to create arrowheads, adding a #3f3f3f to #5e5341 colour gradient overlay. For the fletchings, download the 107167 branches file from CG Textures and change it to red using colour adjustments. Merge the layers and duplicate, then place in the model’s hands.
CREATE A MASK
Use the Pen tool to draw a path that follows the contour of the face with horned extensions. When closed, make a selection of it, add a new layer and fill it with white. Apply shadows to edges to create a 3D effect using a #b7b7b7 coloured soft brush, with the Always Use Pressure For Opacity option activated. Before you start painting shadow, you need to load a selection of the mask, then make a new layer above. Paint to this with a soft brush, creating shadow. Apply Gaussian Blur at a 4px radius, while your mask selection is still active.
HORNS
Creating the horns is a similar process to the mask. First, draw these out using the Pen tool. Then make a selection of the horns and fill this with white in a new layer. Add a Bevel & Emboss Layer Style and set Style to Inner Bevel, Technique to Smooth, Depth at 276%, Size at 13, Soften at 13, Shadow Mode to Multiply, Color to #77979e and Opacity at 38%. Everything else is set to default. Open the ‘Flowers.psd’ supplied on disc and drag this into your working image. Place and transform to build the best look.
WHITE PARTS
Now you will continue to add what looks like bits of porcelain to the model’s skin. First, make use of the Pen tool to make a selection as before, then press Cmd/Ctrl+J to duplicate a skin section. With this duplicated layer selected, go to Image> Adjustment>Desaturate. Load a selection of this shape and apply Gaussian Blur set at a 10px radius. Deselect (Cmd/Ctrl+D) your selection, duplicate this layer twice, then merge all three layers. Go to Levels and input the following values: 15, 1.18 and 228. Apply shadow below the objects using a #926958 coloured brush applied to a new layer set to a Multiply blending mode.
TREES
Trunks can be made with a #c9c9c9 coloured hard brush. A #767676 coloured soft brush is added to
create shadow in the middle of the trunk. Change your brush group to Dry Media. Pick a Soft Oil Pastel brush with a #767676 colour and add lines of varying sizes to the trunk. Download the 55089 trees image from CG Textures and select only the treetop, dragging it into your image. Apply Levels set to 0, 1.88 and 245. Now add Hue/Saturation, setting Saturation at -25. Finally, add Color balance, setting values at 100, 0, +100.
GLOWING EFFECTS
Open the ‘Bird.psd’ file from the disc and drag it into your working image. Create a glow effect behind your model using the Elliptical Marquee tool. Before making your selection, set Feather at 200px. Apply to your background layer and press Cmd/Ctrl+J to duplicate. Add Levels, setting values at 0, 2.08 and 255. Add Color Balance, setting values to 0, 0 and 100. Duplicate your pearls and arrange them at different sizes, floating at the top of the image.
IMPROVE THE MOOD
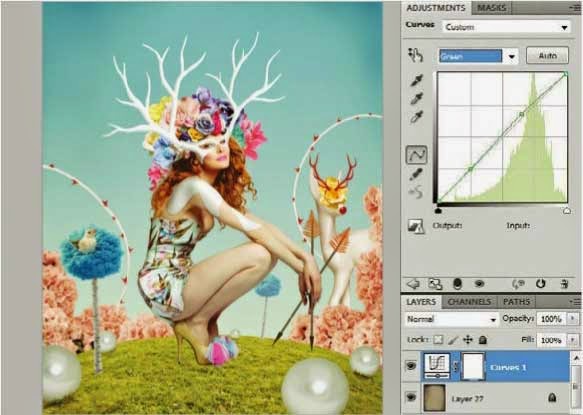
To improve mood and connect the elements together, apply textures and adjustment layers. Open ‘Texture.jpg’ supplied on the disc and drag it into your working image. This layer needs to be above all other layers. Set its blending mode to Soft Light. Add more contrast using Layers>New Adjustment Layer>Curves. Select the Green curves channel and add a slight upwards curve to affect the image colour. See the position in the screenshot below.
IMPROVING GENERAL ATMOSPHERE
Applying textures and layer adjustments is
important, as these tighten up the image and
make all elements look as if they belong in the
same space. Very often an image looks too raw.
Vignette effects in particular focus all elements in
a single space, making the whole image less flat.
Layer adjustments can work to create some
exciting effects, but first and foremost their main
concern is with creating colour harmony, existing
throughout all your layers.
After changing the overall colour and mood, it’s time to polish your image and review all image elements. To make the model’s hair brighter, use the Dodge tool with Exposure set at 70% and pass over this area and darker parts of the dress. To make the model closer to her environment, apply Levels with input set to 0, 1.18 and 255. The grass also looks too dark, so apply Levels with input values set to 0, 1.35, 241. Set output to 11 and 231.
SHADOWS
Adding shadow defines your main light source much better. The most important shadows exist in the grass layer. Choose a #979842 colour and create a new layer. Select a soft brush set to Always Use
Pressure For Opacity and paint in shadows beneath the model, pearls and trees with varying brush sizes. The model’s shoes also need to be darker, so use the Eyedropper tool to choose a darker tone from these. With the same brush settings, make the lower part of the shoes darker.
SUN RAYS
These illustrated sunrays are made in Adobe Illustrator. In a new file, make one straight line with a 1pt stroke. Select Effect>Distort and Transform>Transform. Change Scale/Vertical to 109%, make 40 copies and set Angle at 124°. Turn colour to white and drag objects into your image. Resize this new vector layer then Rasterize it (Cmd/Ctrl-click layer> Rasterize layer). To avoid sharp ends in your lines, apply a soft brush Erase tool and erase the tops of these with one click.
♦ QUICK TIP
Take care of light and it will take care of the rest, making your image much more convincing. All newly imported images and elements need to be edited so that they follow one light source.


































































Follow Us
Were this world an endless plain, and by sailing eastward we could for ever reach new distances